Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Success Ratio of OAP Treatment
- Understanding Pierre Robin Sequence
- Challenges in Treating Pierre Robin Sequence
- The Stanford Orthodontic Airway Plate (OAP)
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Benefits of Non-Surgical Treatment
- FAQs about OAP Treatment
- Conclusion
- References
The Stanford Orthodontic Airway Plate
Pierre Robin Sequence (PRS) is a rare condition that affects infants, causing difficulties in breathing and feeding. Traditionally, surgical treatments have been used to manage PRS, but they come with risks and long-term effects. A groundbreaking non-surgical treatment, the Stanford Orthodontic Airway Plate (OAP), offers a safer and effective alternative. This article explores the benefits, process, and success stories of using OAP to treat PRS.
Success Ratio of OAP Treatment
The success ratio of OAP treatment is highly encouraging. A study involving 433 infants treated with OAP over 20 years demonstrated that:
- 100% of infants with isolated PRS overcame their breathing difficulties without surgery.
- 83% of infants with syndromic PRS also overcame breathing issues using OAP alone or in combination with noninvasive respiratory support .
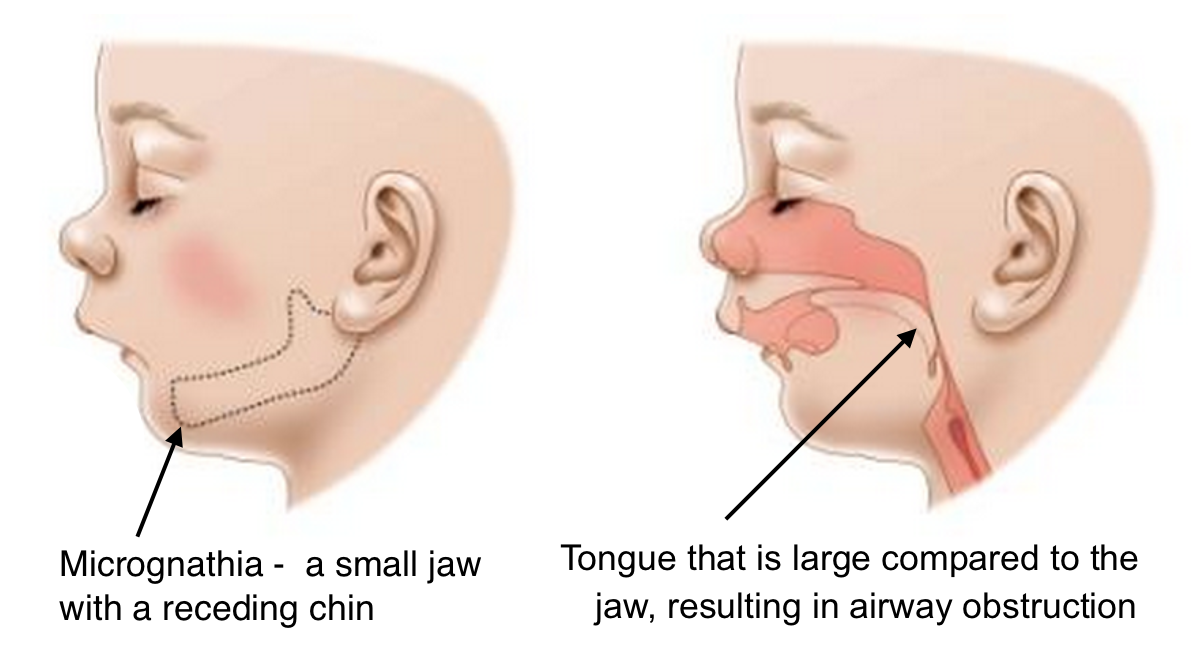
Understanding Pierre Robin Sequence
Pierre Robin Sequence is characterized by three main symptoms:
- Mandibular Retrognathia: A small lower jaw that is set back from the upper jaw.
- Glossoptosis: The tongue falls back into the throat, obstructing the airway.
- Upper Airway Obstruction (UAO): Difficulty in breathing due to airway blockage.
About 80-90% of babies with PRS also have a cleft palate, making feeding even more challenging.
Challenges in Treating Pierre Robin Sequence
Traditional Treatments
Traditional methods include both non-surgical and surgical options:
- Non-Surgical: Prone positioning, nasopharyngeal airway (NPA), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), and high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC).
- Surgical: Glossopexy, mandibular distraction osteogenesis (MDO), and tracheostomy.
Limitations
- Surgical Risks: Repeated general anesthesia, damage to developing structures, and long-term adverse effects.
- Non-Surgical Limitations: May not always be effective in severe cases.
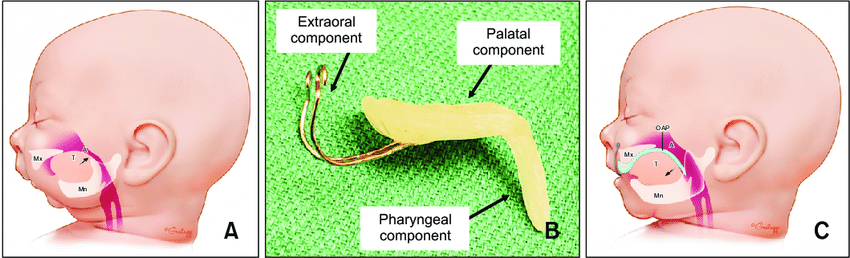
The Stanford Orthodontic Airway Plate (OAP)
How OAP Works
The OAP is a custom-made device consisting of intraoral, intrapharyngeal, and extraoral components. It helps to keep the tongue in the correct position and promotes jaw growth, ensuring an open airway.
Process of Fabrication and Use
- Maxillary Imprint: A mold of the baby’s upper jaw is taken.
- Creating the OAP: The OAP is custom-made based on the mold.
- Fitting: The device is fitted and adjusted using nasopharyngoscopy to ensure it works properly.
- Daily Use: The OAP is worn continuously, removed only for cleaning.
Table: Comparison of Traditional and OAP Treatments
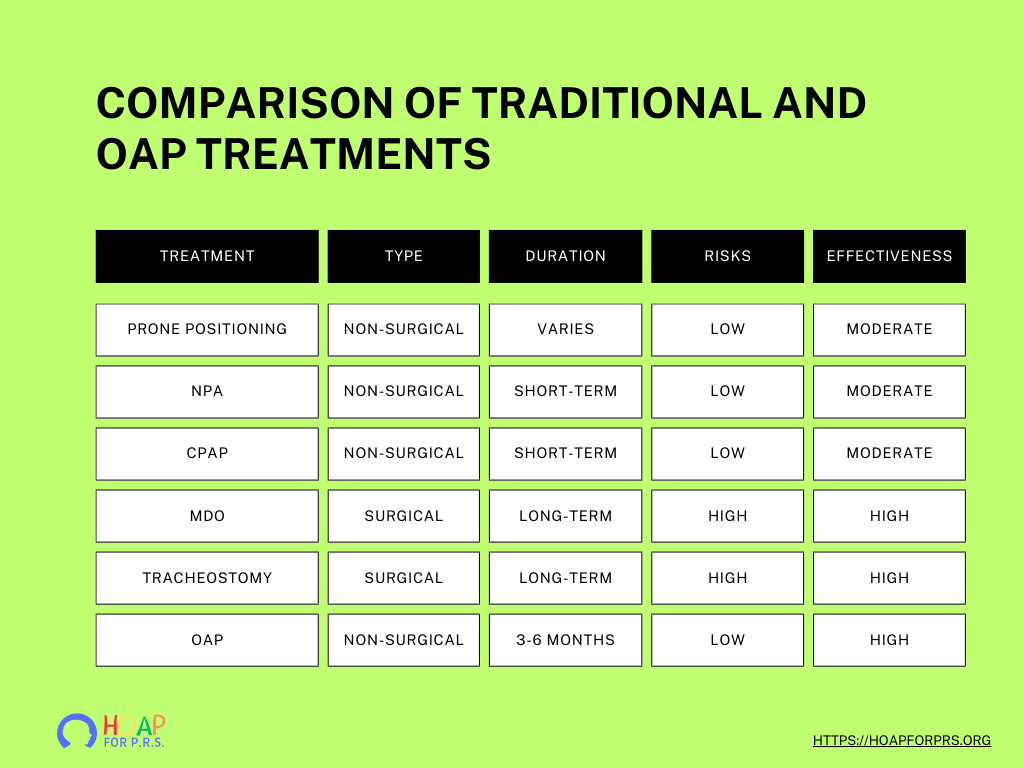
Benefits of OAP
- Non-Invasive: No surgery required.
- Effective: Immediate improvement in breathing and feeding.
- Short Duration: Typically worn for 3-6 months.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Case #1
- Profile: A 5-week-old boy with severe feeding difficulties and airway obstruction.
- Results: Significant improvement in airway stability and feeding. Stable weight gain and improved respiratory indices.
- Stats:
- Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) reduced from 69.6 to 10.3.
- Mixed Obstructive Apnea Index (MOAI) reduced from 35.4 to 3.
Case #2
- Profile: A 5-week-old girl with late presentation of UAO.
- Results: Improved airway stability and feeding. Positive developmental outcomes.
- Stats:
- AHI reduced from 15.4 to 3.3.
- MOAI reduced to 0.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Treatment
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Infants and families experience less stress and faster recovery.
- Lower Risk: No surgical risks involved.
- Cost-Effective: Reduced need for hospital stays and surgical procedures.
FAQs about OAP Treatment
What is Pierre Robin Sequence (PRS)?
PRS is a condition that causes a small lower jaw, tongue displacement, and airway obstruction in infants.
How does the Orthodontic Airway Plate (OAP) help?
The OAP positions the tongue correctly and promotes jaw growth, keeping the airway open and improving breathing and feeding.
Is the OAP treatment safe?
Yes, it is a non-surgical and safe treatment with no need for general anesthesia.
How long does the OAP treatment take?
The treatment typically takes 3-6 months.
Are there any risks associated with OAP treatment?
The risks are minimal compared to surgical options. Regular monitoring ensures the device fits correctly and functions as intended.
Conclusion
The Stanford Orthodontic Airway Plate (OAP) offers a revolutionary non-surgical treatment for infants with Pierre Robin Sequence. By promoting jaw growth and maintaining an open airway, the OAP significantly improves breathing and feeding, enhancing the quality of life for affected infants and their families. Increased awareness and adoption of this treatment can provide a safer, effective alternative to traditional surgical methods.
References
- Choo, H., Khosla, R. K., Meister, K. D., et al. (2022). Nonsurgical Orthodontic Airway Plate Treatment for Newborns With Robin Sequence. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal, 59(3), 403-410. doi:10.1177/10556656211007689
- Choo, H., Galera, R. I., Balakrishnan, K., et al. (2023). Disruptive Therapy Using a Nonsurgical Orthodontic Airway Plate for the Management of Neonatal Robin Sequence: 1-Year Follow-up. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal, 60(6), 758-767. doi:10.1177/10556656221076980


